
How to Manage Project Dependencies with Git Submodules
Imagine you are building a website, and you want to include a third-party JavaScript library. You could download the library and copy it into your project, but what happens when that library gets updated? You would have to repeat the process manually.
Git's "submodule" feature provides an elegant solution. It allows you to keep a Git repository as a subdirectory inside your main project repository, while keeping their histories separate.
When Are Submodules Useful?
Submodules are a great choice when you need to:
- Include a component or library from a third-party that is still under active development.
- Separate a large project into smaller, more manageable components.
- Share code between different projects without duplicating it.
How to Work with Submodules
Let's walk through the essential commands for managing submodules.
1. Adding a New Submodule
To add a new submodule, you use the git submodule add command. This will add the specified repository into your project at the given path.
$ git submodule add https://github.com/some-user/some-library.git assets/vendor/some-library
This command does two things:
- It creates a
.gitmodulesfile in your project root, which tracks the submodule's URL and path. - It adds the submodule directory to your index, "locked" at a specific commit.
You must then commit this change: git commit -m "Add the 'some-library' submodule".
2. Cloning a Project with Submodules
If you clone a project that contains submodules, you need to tell Git to download them as well.
The easiest way is to use the --recurse-submodules flag when cloning:
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/your-user/your-project.git
If you forgot to do that, you can initialize the submodules at any time with:
$ git submodule init
$ git submodule update
3. Updating a Submodule
To get the latest version of a submodule, you need to perform two steps. First, go into the submodule's directory and pull the latest changes from its remote. Then, return to the parent project and commit the updated submodule reference.
$ cd assets/vendor/some-library
$ git pull origin main
$ cd ../../..
$ git commit -am "Update the 'some-library' submodule to the latest version"
This "locks" the submodule to the new, updated commit.
4. Pulling Updates That Include a Submodule Change
If you pull changes from your main project's remote and a teammate has updated a submodule, your local submodule will not be updated automatically.
You must run git submodule update --recursive to bring the submodule files in line with the commit your main project now references.
Tip
Handling Submodules with Ease in Tower
Managing submodules from the command line can be complex. The Tower Git client simplifies this process immensely.
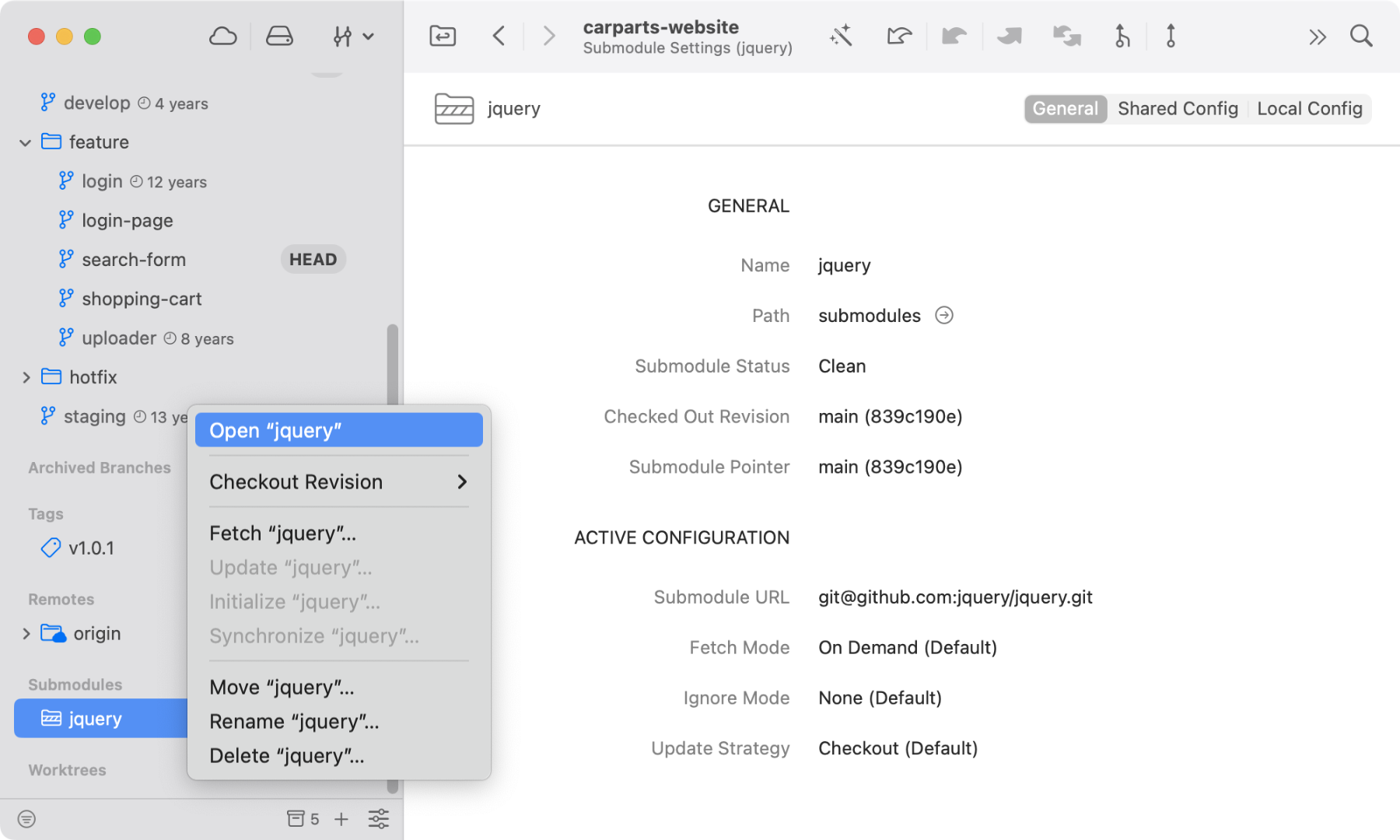
Tower automatically detects submodules and clearly displays their status. You can fetch, update, and commit submodule changes with a few clicks, avoiding the need to navigate directories and run multiple commands.
Learn More
- Dive deeper with the official Git documentation on Git Submodules
- Explore more advanced topics in our free online book
Get our popular Git Cheat Sheet for free!
You'll find the most important commands on the front and helpful best practice tips on the back. Over 100,000 developers have downloaded it to make Git a little bit easier.

About Us
As the makers of Tower, the best Git client for Mac and Windows, we help over 100,000 users in companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, Twitter, and Ebay get the most out of Git.
Just like with Tower, our mission with this platform is to help people become better professionals.
That's why we provide our guides, videos, and cheat sheets (about version control with Git and lots of other topics) for free.