
How (and Why) to Sign Commits with GPG
You've probably seen a green "Verified" badge next to commits on GitHub and wondered what it means. This badge is a sign of trust: it confirms the commit was created by a verified author and hasn't been tampered with. This verification is achieved by cryptographically signing your commits with a GPG key.
Let's explore why this is important and how you can set it up for your own projects.
Why Sign Your Commits?
Think of a signed commit as a digital signature on a legal document. It provides a layer of security and authenticity that is crucial, especially in collaborative and open-source environments.
- Authenticity: It proves that the commit was made by you. Someone else cannot push code to a project under your name.
- Integrity: It ensures that the code has not been altered since it was committed. The commit's content and its signature are cryptographically linked.
- Trust: For project maintainers, signed commits provide confidence that the code they are merging comes from a trusted source.
How to Sign Your Commits
Here is a step-by-step guide to start signing your commits.
1. Install GPG
First, you need the GPG command-line tools. You might already have them installed.
- macOS: The easiest way is via Homebrew:
brew install gnupg - Windows: You can download and install Gpg4win by following our guide.
- Linux: It's typically available via your package manager:
sudo apt-get install gnupg
2. Generate a GPG Key
Next, you need to generate your own unique key.
$ gpg --full-generate-key
You will be guided through a series of prompts. It's generally safe to accept the default suggestions. Make sure that the email address you use is the same one associated with your Git and GitHub account.
3. Configure Git with Your Key
After creating the key, you need to tell Git which key to use. First, list your keys to get the Key ID:
$ gpg --list-secret-keys --keyid-format=long
/Users/bruno/.gnupg/pubring.kbx
---
sec rsa4096/012ACBE2282B9183 2025-02-07 [SC] [expires: 2028-02-07]
7A3B3006AC6FBC26FF6DAA05011ECBE7162A9183
uid Bruno Brito (bruno@git-tower.com)
Copy the GPG key ID that starts with rsa4096/. In the example above, it's 012ACBE2282B9183. Then, configure Git:
$ git config --global user.signingkey 012ACBE2282B9183
4. Add Your Public Key to GitHub
To get the "Verified" badge, you need to tell GitHub (or GitLab/Bitbucket) about your public key. Export your public key:
$ gpg --armor --export 012ACBE2282B9183
Copy the entire output (starting with -----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----) and add it as a new GPG key in your GitHub account's "SSH and GPG keys" settings.
5. Start Signing!
You can now sign a commit using the -S flag.
$ git commit -S -m "My first signed commit"
To make signing the default for all commits in the future, you can set the following global configuration:
$ git config --global commit.gpgsign true
Now, all your future commits will be signed automatically!
Tip
Signing Commits with Ease in Tower
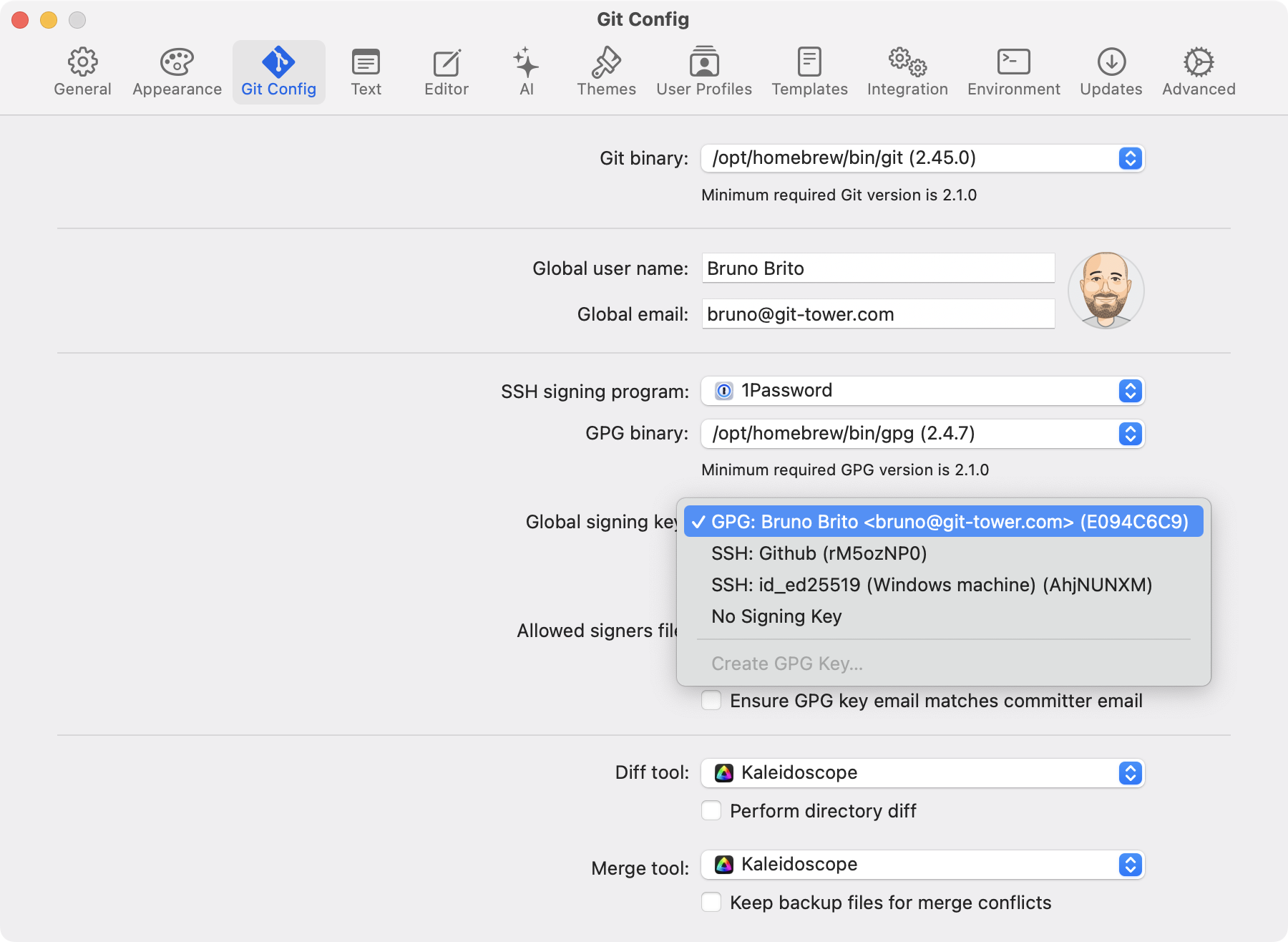
If you prefer a simpler approach, the Tower Git client makes commit signing effortless. Tower automatically detects your GPG keys, and once configured, you can sign a commit with a single click — no need to remember commands or flags.
To get started, simply head over to the "Git Config" tab in Tower's Settings. This seamless integration makes security a simple and natural part of your workflow.
Learn More
- Read the official GitHub documentation on Signing Commits
- Explore advanced Git topics in our free online book
Get our popular Git Cheat Sheet for free!
You'll find the most important commands on the front and helpful best practice tips on the back. Over 100,000 developers have downloaded it to make Git a little bit easier.

About Us
As the makers of Tower, the best Git client for Mac and Windows, we help over 100,000 users in companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, Twitter, and Ebay get the most out of Git.
Just like with Tower, our mission with this platform is to help people become better professionals.
That's why we provide our guides, videos, and cheat sheets (about version control with Git and lots of other topics) for free.